

Please follow these steps to file a notice:Ī physical or electronic signature of the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf Īn identification of the copyright claimed to have been infringed Ī description of the nature and exact location of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright, in \ On or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, you should consider first contacting an attorney. Thus, if you are not sure content located Misrepresent that a product or activity is infringing your copyrights. Please be advised that you will be liable for damages (including costs and attorneys’ fees) if you materially Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such Means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors. Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to Information described below to the designated agent listed below. Or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice (“Infringement Notice”) containing If you believe that content available by means of the Website (as defined in our Terms of Service) infringes one

Therefore we arrive at the conclusion that The final result is obtained by canceling the factor and using the triginometric identity: Substituting in for in the first equation will give us the following: Thus the normal force is equal to the cosine component of the weight. Solving for in the second equation gives us. Plugging these values into the force equations above gives us the following equations: Summing all the forces in the y-direction gives us Summing all the forces in the x-direction gives us Plugging these accelerations in, we find that and Also, because the block moves at constant velocity down the plane, Newton's 1st law assures us that there is no acceleration in the x direction as well, therefore. Newton's 2nd law gives us two equations:īecause the block is constrained to move along the surface of the inclined plane, there should be no acceleration in the y direction, and so. Now we can use Newton's 2nd law to relate the given forces above. However, the weight is not along either of these axes, so we resolve the force into its components, along the negative y-axis, and along the positive x-axis. Thus the friction force points in the negative direction of the x-axis, and the normal force is aligned with the positive direction of the y-axis. We choose a coordinate system so that our x-axis aligns with the motion of the block down the plane, and the y-axis aligns with the direction of the normal force. Third, the friction force, which acts opposite to its direction of motion and is given as.

Second, the normal force of the plane, which is given as. First, it's weight under the influence of gravity, which is given as. This block has three forces acting on it.
The free body diagram of the block is given above. The only force acting on the 30 kg block is the tension, and the acceleration is what we found above. ĭo this by using Newton's second law again, except for only one of the blocks: Now that we have acceleration, we need to write a new equation in which the tension force does not cancel out so that we can solve for the tension. We can solve for acceleration, since the tensions cancel out. In this problem, the two tension forces form an action/reaction pair and therefore are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction (Newton's third law).
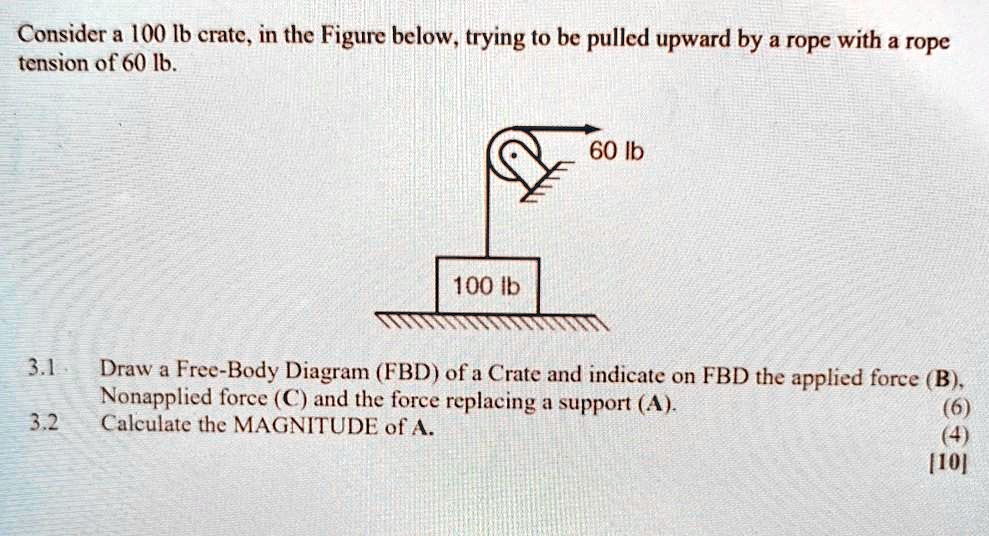
#Ib free body diagram plus#
Since the blocks are connected by a string, they will therefore accelerate at the same rate, and we can treat them as a system that moves as if it were one object of total mass 80 kg (30 kg plus 50 kg). We are given in the question that the force is 100 N. You could also draw in the force of gravity and the normal force for each block, but they have been omitted from the image because they cancel each other out for each block and because there is no friction in this problem. Start by drawing in the forces acting on each block.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
